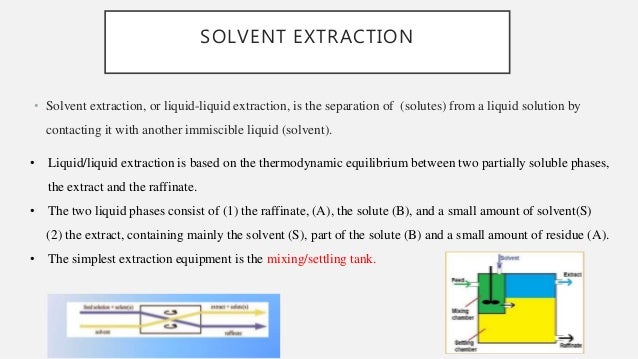
Liquid liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids usually water and an organic solvent.
Liquid liquid extraction equipment ppt.
The organic mixture is fed counter current to the extraction solvent water.
Unit operations lab ii.
Liquid liquid extraction experiment 350 ech4404l.
Liquid liquid extraction also called solvent extraction was initially utilized in the petroleum industry beginning in the 1930 s.
There is a net transfer of one or more species from one liquid into another liquid phase generally from aqueous to organic.
Leaching occurs in two steps.
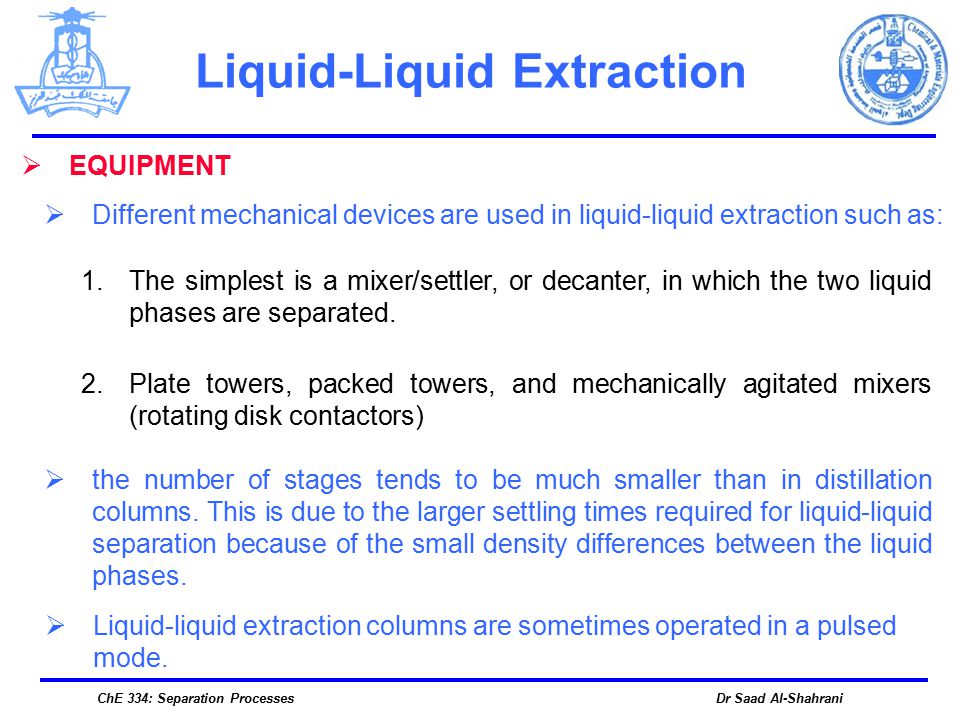
As in the separation processes of absorption and distillation the two phases in liquid liquid extraction must be brought into intimate contact with a high degree of turbulence in order to obtain high mass transfer rates.
Todd idaho national laboratory.
Liquid liquid extraction is a method by which a compound is pulled from solvent a to solvent b where solvents a and b are not miscible.
Thus extraction can be performed at low temperatures.
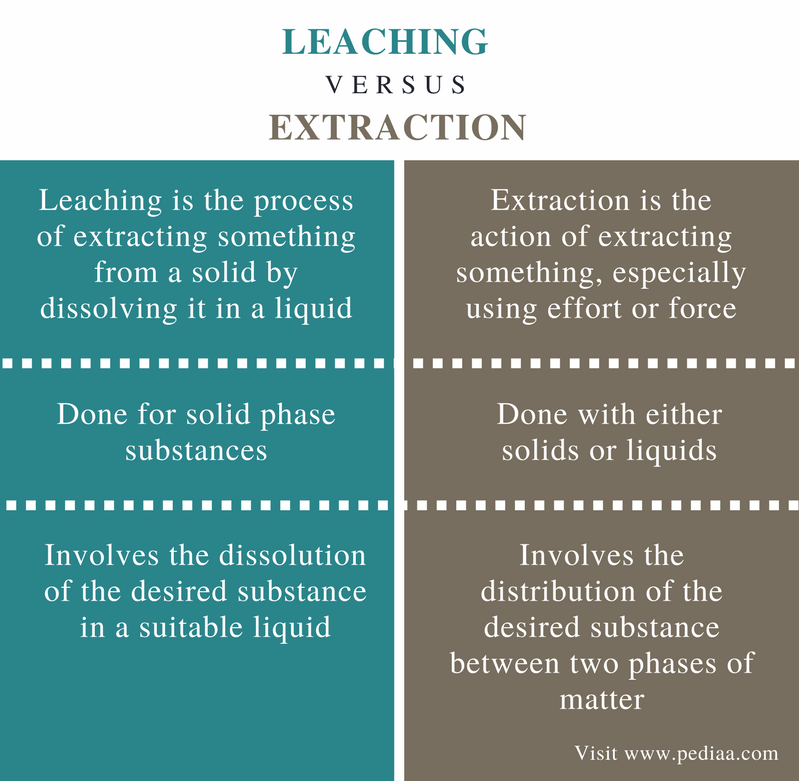
Solid liquid extraction leaching leaching.
Packed extractor design hydraulics packed extractor design mass transfer extraction equipment selection depends on.
Liquid liquid extraction equipment jack d.
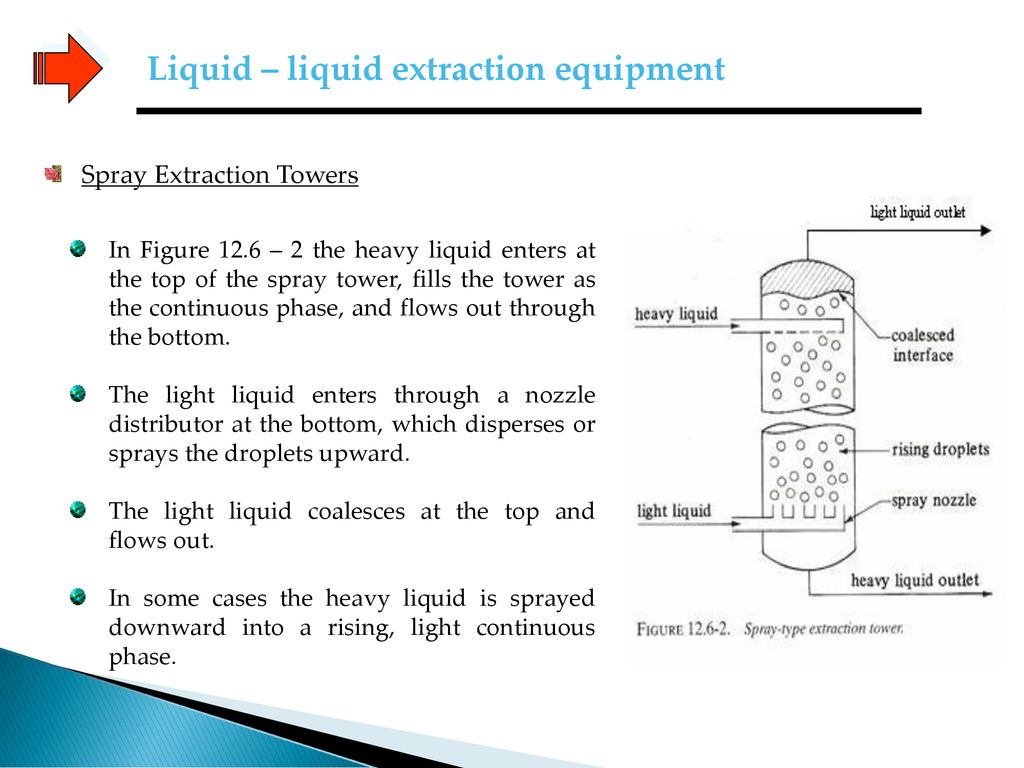
Types of equipment and design for liquid liquid extraction 12 6a.
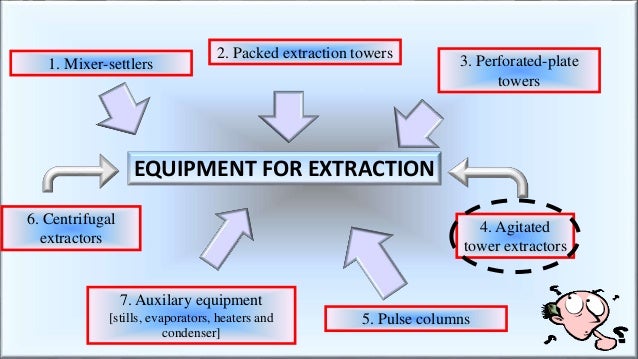
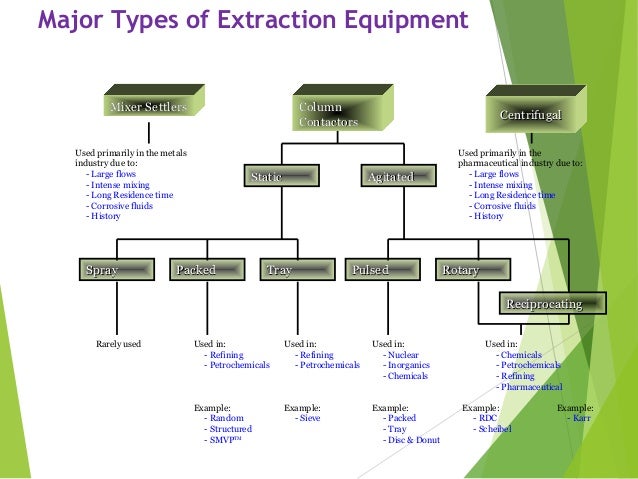
Introduction and equipment types.
It has since been utilized in numerous applications including.
The equilibrium data for a liquid liquid system are of vital importance in the selection and design of an extraction equipment.
The separation of the solution from the remaining solid washing.
Contacting solvent and solid to effect a transfer of a solute leaching.
Liquid liquid extraction lle also known as solvent extraction and partitioning is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids usually water polar and an organic solvent non polar.
2 extraction processes.
It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid phase into another liquid phase.
Solvent recovery economics viscosities interfacial tension solids product solvent value flowrates risk assessment operation experience static columns a spray tower packed tower static columns light liquid out.
Extraction is a process where one or more solute s are removed from one liquid phase technically called a diluent by transferring that those the solute s to another liquid phase or a solvent since this is the operation between the two liquid phases no vaporisation is needed.
Factors influencing the rate of.
Liquid liquid extraction with solvents more dense than water.
Law and terry a.